Blaze Star
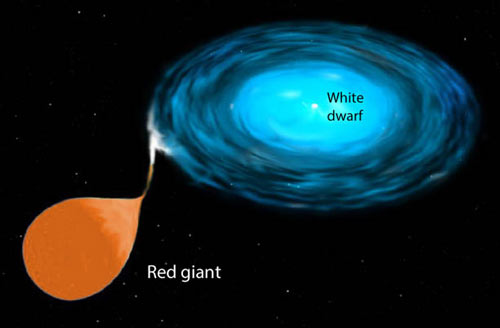
Stars like T CrB involve a red giant closely paired with a white dwarf. The giant feeds hydrogen gas into a swirling accretion disk around a massive, compact white dwarf at a rate a million times greater than the solar wind. Material funnels from the disk onto the dwarf's surface until it ignites in a thermonuclear explosion similar to a nova.
Blaze Star is the popular name for the recurrent nova T Coronae Borealis (see constellation Corona Borealis) of which two major outbursts have been observed: in 1866 and 1946, when it rose rapidly to the second and third magnitude, respectively, before slowly returning to its quiescent magnitude of 10.8. Other, smaller increases in brightness have been recorded at ultraviolet wavelengths. The star is a spectroscopic binary with a red giant component and a period of 227.6 days.


