birth
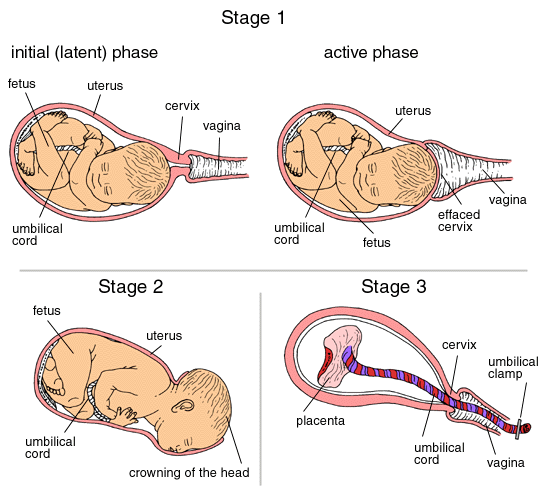
The three stages of labor.
Birth is the emergence from the mother's uterus (womb), or, in the case of lower animals, from the ovum (egg), marking the beginning of an independent life. The birth process is triggered by hormone changes in the mother's bloodstream. Birth may be induced, if required, by oxytocin.
Mild labor pains (contractions of the uterus) are the first signs that a woman is about to give birth. Initially occurring about every 20 minutes, in a few hours they become stronger and occur every few minutes. This is the first stage of labor, usually lasting about 14 hours. The contractions push the baby downward, usually head first, which breaks the membranes surrounding the baby, and the amniotic fluid escapes.
In the second stage of labor, stronger contractions push the baby through the cervix (neck of the uterus) and vagina. This is the most painful part and lasts less than 2 hours. Anesthetics or analgesics are usually given, and delivery aided by hand or obstetric forceps. A cesarean section may be performed if great difficulty occurs. Some women choose natural childbirth, in which no anesthetic is used, but pain is minimized by prior relaxation exercises.
As soon as the baby is born, its nose and mouth are cleared of fluid and breathing starts, whereupon the umbilical cord is cut and tied. In the third stage of labor the placenta is expelled from the uterus and bleeding is stopped by further contractions. Birth normally occurs 38 weeks after conception. Premature births are those occurring after less than 35 weeks. Most premature babies develop normally with medical care, but if born before 28 weeks the chances of survival are poor.
Birth canal
The birth canal is the passage, extending from the cervix to the introitus (opening of the vagina), through which the baby passes during childbirth.
Birth defect
A birth defect is a structural, functional, or metabolic abnormality present at birth that results in physical or mental disability or is fatal. There are more than 4,000 known birth defects, which may be caused by genetic or environmental factors. About 150,000 babies are born each year with birth defects.
Cesarian section
A cesarian section, also known as C-section, is the birth of a child from the uterus (womb) by abdominal operation. The mother is given an anesthetic and an incision is made in the abdomen and lower part of the uterus; the child is delivered and attended to; the placenta is removed and incisions are sewn up.
Cesarian section may be necessary if the baby is too large to pass through the pelvis, if it shows delay or signs of anoxia during labor, or in cases where maternal disease does not allow normal labor. It may be performed effectively before labor has started. With modern anesthesia and blood transfusion, the risk of cesarian section are not substantially greater than those of normal delivery. It is believed that Julius Caesar was born in this way.


