cardiac CT
Cardiac CT scanner. Credit: Christiana Care.
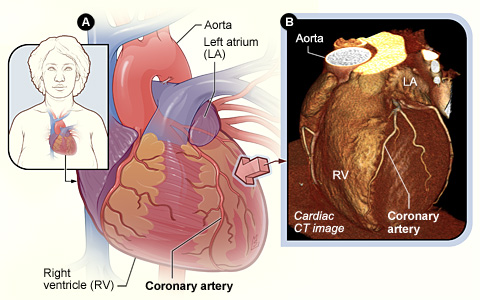
Figure A shows the position of the heart in the body. The arrow shows the point of view of the cardiac CT image. Figure B is a cardiac CT image showing the coronary arteries on the surface of the heart. This is a picture of the whole heart, put together by the computer.
Cardiac computed tomography, or cardiac CT, is a painless test that uses an X-ray machine to take clear, detailed pictures of the heart. It's a common test for showing problems of the heart. During a cardiac CT scan, the X-ray machine moves around the patient's body in a circle and takes a picture of each part of the heart. Cardiac CT is a specific type of computed tomography.
Because an X-ray machine is used, cardiac CT scans involve radiation. However, the amount of radiation used is small. This test gives out a radiation dose similar to the amount of radiation a person is naturally exposed to over 3 years. There is a very small chance that cardiac CT will cause cancer.
Each picture that the machine takes shows a small slice of the heart. A
computer puts the pictures together to make a large picture of the whole
heart. Sometimes an iodine-based dye is injected into one of the veins during
the scan to help highlight blood vessels and arteries on the X-ray images.
What to expect before cardiac CT
A patient is given instructions before the cardiac computed tomography (CT) scan. Usually he or she be will asked to avoid drinks that contain caffeine before the test. Normally the patient will be able to drink water, but won't be able to eat for 4 hours before the scan.
Patients who take medicines for diabetes should ask their doctor whether they will need to change how they take them on the day of the cardiac CT scan.
The doctor needs to know if the patient:
Patients will be asked to remove their clothes above the waist and wear a hospital gown. They will also be asked to remove any jewelry from around their neck or chest.
Taking pictures of the heart can be difficult because the heart is always beating (in motion). A slower heart rate will help produce better quality pictures. If the patient doesn't have asthma or heart failure, he or she may given a medicine called a beta blocker to help slow the heart rate. The medicine will be given by mouth or injected into a vein.
During cardiac CT
The cardiac computed tomography (CT) scan will take place in a hospital or outpatient office. Because an X-ray machine is used, cardiac CT scans involve radiation. However, the amount of radiation used is small. This test gives out a radiation dose similar to the amount of radiation a person is naturally exposed to over 3 years. There's a very small chance that cardiac CT will cause cancer. A doctor who has experience with CT scanning will supervise the test.
If the doctor wants to use contrast dye during the cardiac CT scan, a small needle connected to an intravenous (IV) line will be put in a vein in the hand or arm.
The contrast dye will be injected through the IV during the scan. The patient may have a warm feeling during the injection. The dye will highlight the blood vessels on the X-ray pictures from the cardiac CT scan.
The technician who operates the cardiac CT scanner will clean areas of the chest and place small sticky patches on those areas. The patches are attached to an EKG (electrocardiogram) machine to record the electrical activity of the heart during the exam.
The CT scanner is a large, square machine that has a hollow, circular tube in the middle. The patient lies on his or her back on a sliding table that can move up and down and goes inside the tunnel-like machine.
Inside the scanner, an X-ray tube moves around the patient's body to take pictures of different parts of the heart. These pictures can be shown on a computer as one large, three-dimensional picture. The technician controls the machine from the next room. The technician can see the patient through a glass window and talk to him or her through an intercom system.
Moving the body can cause the pictures to blur. The patient will be asked to lie still and hold his or her breath for short periods, while each picture is taken.
A cardiac CT scan usually takes about 15 minutes to complete. However, it can take over an hour to get ready for the test and for the medicine to slow the heart rate enough.
After cardiac CT
Once the cardiac computed tomography (CT) scan is done, the patient is able to return to your normal activities.
A doctor who has experience with CT will provide the patient's doctor with the results of the test so that these can be conveyed to the patient.
What does cardiac CT show?
Many X-rays are taken while the patient is in the computed tomography (CT) scanner. Each picture that the machine takes shows a small slice of the heart. A computer can put the pictures together to make a large picture of the whole heart. This picture shows the inside of the heart and the structures that surround the heart.
Cardiac CT is a common test for finding and evaluating:
- Aneurysms, which are diseased areas of a weak blood vessel wall that bulge out. Aneurysms can be life threatening because they can burst.
- Dissections, which can occur when the layers of the aortic artery wall peel away from each other. This condition can cause pain and also may be life threatening.
Because the heart is in motion, a fast type of CT scanner, called multidetector computed tomography (MDCT), is used to show high-quality pictures of the heart.
Another type of CT scanner, called electron-beam computed tomography (EBCT), is used to detect calcium in the coronary arteries. Calcium in the coronary arteries may be an early sign of coronary artery disease (CAD).
CAD occurs when the coronary arteries (the arteries that supply blood and oxygen to the heart muscle) harden and narrow due to the buildup of a material called plaque (plak) on their inner walls. CAD is the leading cause of death for both men and women in the United States.
Researchers also are studying new ways to use cardiac CT.
Risks
Cardiac computed tomography (CT) scans are safe, painless tests. Although cardiac CT uses radiation, the amount is small.
Some people feel side effects from the contrast dye that's used during the cardiac CT scan, including the following:
People who have asthma or emphysema may have breathing problems during cardiac CT if they're given beta blockers to slow down their heart rates.


