contrast medium
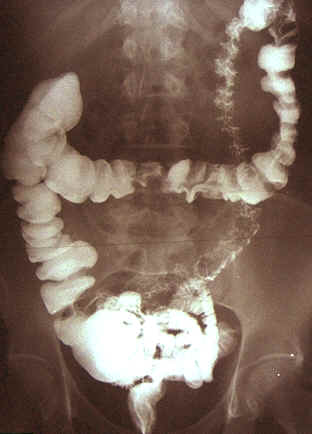
X-ray of the lower GI with barium contrast.
A contrast medium, also called a contrast agent or contrast material, is a substance introduced into the body in order to create a difference in the apparent density of various organs and tissues, thus making it easier to delineate adjacent body tissues and organs. Contrast media are used in conjunction with various medical imaging techniques, including X-rays, computed tomography (CT) scanning, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Contrast media are administered in different ways. Some are given as a drink, others are introduced through an intravenous line or an enema. After the examination, some contrast agents are harmlessly absorbed by the body; others are excreted through the urine or bowel movements. Contrast media are not dyes and do not permanently discolor internal organs. Rather, they temporarily change the way X-rays or other imaging tools interact with different tissues and organs.
Radiocontrast agents
Radiocontrast agents are contrast media used with X-ray imaging techniques such as radiography (conventional X-rays) and computed tomography. These agents fall in to two main categories: barium-based and iodine-based.
Barium in the form of barium sulfate is mainly used in imaging the gastrointestinal system. Barium blocks the passage of X-rays, so barium-filled organs stand out better on X-ray exams. For an examination of the esophagus or stomach, patients are asked to drink a mixture of barium sulfate and water, sometimes with vanilla or fruit flavoring added. This mixture usually is thick and white, and is sometimes called a barium meal. For an examination of the rectum or colon, barium is administered rectally through an enema tube.
Contrast agents containing iodine are used to image the gallbladder, urinary tract, blood vessels, spleen, liver, and bile duct. Iodine contrast agents are clear liquids and usually are injected.
MRI contrast agents
MRI contrast agents are a group of contrast media used to improve the visibility of internal body structures in magnetic resonance imaging. The most commonly used compounds for contrast enhancement are gadolinium-based.


