electrophoresis
Motion by electrophoresis of a charged particle.
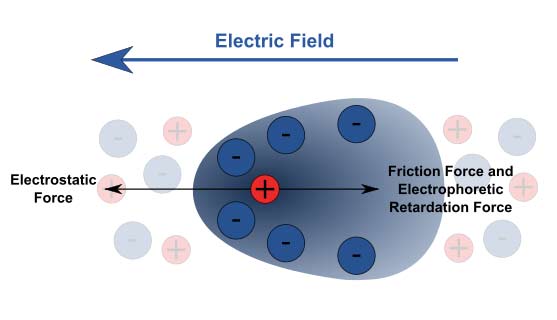
Electrophoresis is the diffusion of charged particles through fluids or gels (firm jelly-like substances)
under the influence of an electric field.
Particles with different sizes and charges diffuse at different rates, so
that the effect can be used to separate and identify large molecules, such
as proteins or fragments of DNA or RNA. The current forces the molecules through
pores in a thin layer of gel, which is made so that its pores are just the
right dimensions for separating molecules within a specific range of sizes
and shapes. Smaller fragments usually travel further than large ones. The
process is sometimes called gel electrophoresis. It is
widely used to analyze body chemicals such as the various proteins in blood
serum.


