foot

Figure 1. Bones of the foot seen from the side.

Figure 2. Bones of the foot seen from above.
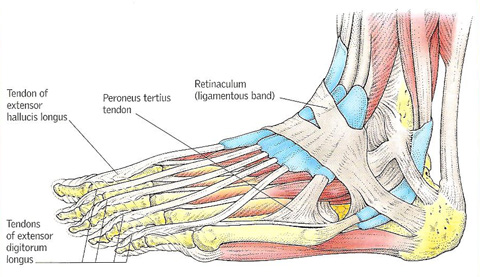
Figure 3. Tendons of the foot. Long tendons reach down the foot from the muscles at the front and back of the leg, allowing the ankle and the hinge joints of the toes to be flexed and extended.
The foot is the terminal part of the leg of humans and other vertebrates upon which the individual stands and walks. The foot supports the weight of the body in standing or walking, and acts as a lever to propel the body forward.
The human foot is a complex structure made up of 26 bones and 33 joints that are moved by a combination of 19 muscles and 107 ligaments.
The bones of the foot are arranged in three natural groups:
Structure of the foot
The largest bone of the foot, the heel-bone (the calcaneus) is jointed with the ankle bone (the talus). The tarsal bones are located in front of the talus and calcaneus and are jointed to five metatarsal bones. The bones of the toes are called the phalanges; the big toe has two phalanges and all the remaining toes have three.
Tendons passing around the ankle connect the muscles that act on the various bones of the foot and toe. The main blood vessels and nerves pass in front of and behind the inside of the ankle to supply the foot. The undersurface of a normal foot forms a natural arch that is supported by ligaments and muscles. Fascia (fibrous tissue) and fat form the sole of the foot, which is covered by a layer of tough skin.
Disorders of the foot
Injuries to the foot often result in fractures to the foot bones (the metatarsals and phalanges). The calcaneus may fracture following a fall from a height on to a hard surface.
Congenital foot abnormalities are fairly common and include clubfoot (talipes), flat-feet, and claw-foot. A bunion is a common deformity of the foot in which a thickened bursa (fluid-filled pad) lies over the joint at the base of the big toe.
Corns are small areas of thickened skin that are usually caused by tightly fitting shoes. Verrucas develop on the soles of the feet. Athlete's foot is a fungal infection that affects the skin between the toes, causing it to become very itchy, sore, and cracked.
 |
| Cross-section of a corn. A plug of dead skin cells extends through the epidermis into the dermis, which has a nerve supply. Pressure on the plug can cause pain. |
Gout is a relatively common type of arthritis that often affects the joint at the base of the big toe or one of the joints in the foot. An ingrowing toenail commonly occurs on the big toe and may lead to inflammation and infection of the surrounding tissues.
Foot-drop is the inability to raise the foot properly causing it to drag along the ground when the person is walking. The condition may occur as a result of damage to the muscles in the leg that are responsible for performing this movement or, alternatively, to the nerves that supply these muscles.


