Pioneer 7
Pioneer 6, 7, 8, and 9.
Pioneer 7 was the second of four identical solar orbiting, spin-stabilized spacecraft – Pioneer 6, 7, 8, and 9 – in the Pioneer series of deep space probes. Pioneer 7, launched on 17 August 1966, was last tracked successfully on 31 March 1995. At that time, the spacecraft and one of its science instruments were still functioning.
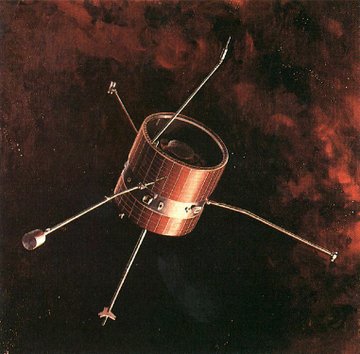
Pioneer 7''s main body is an aluminum cylinder 94 centimeters (37 inches) in diameter and 89 centimeters (35 inches) long. There are three magnetometer booms, each 208 centimeters (82 inches) long. The antenna mast (pointing down in the picture) is 132 centimeters (52 inches) long. The mass is approximately 63 kilograms (138 pounds). 79 watts of power was generated from the solar panels. The spacecraft is spin-stabilized at approximately 60 rpm, with the spin axis perpendicular to the plane of the ecliptic.
Pioneers 6–9 demonstrated the practicality of spinning a spacecraft to stabilize it and to simplify control of its orientation. Measurements made by these spacecraft greatly increased our knowledge of the interplanetary environment and the effects of solar activity on Earth. New information was gathered about the solar wind, solar cosmic rays, the structure of the Sun's plasma and magnetic fields, the physics of particles in space, and the nature of storms on the Sun which produce solar flares. This series of spacecraft also discovered Earth's magnetotail (magnetic field tail away from the Sun).
| launch date | Aug 17, 1966 |
| launch vehicle | Delta E1 |
| launch site | Cape Canaveral |
| orbit | solar; periapsis 1.009 AU; apoapsis 1.125 AU; period 402.9 d; inclination 0.098° eccentricity 0.054 |
| other designations | Pioneer-B |


